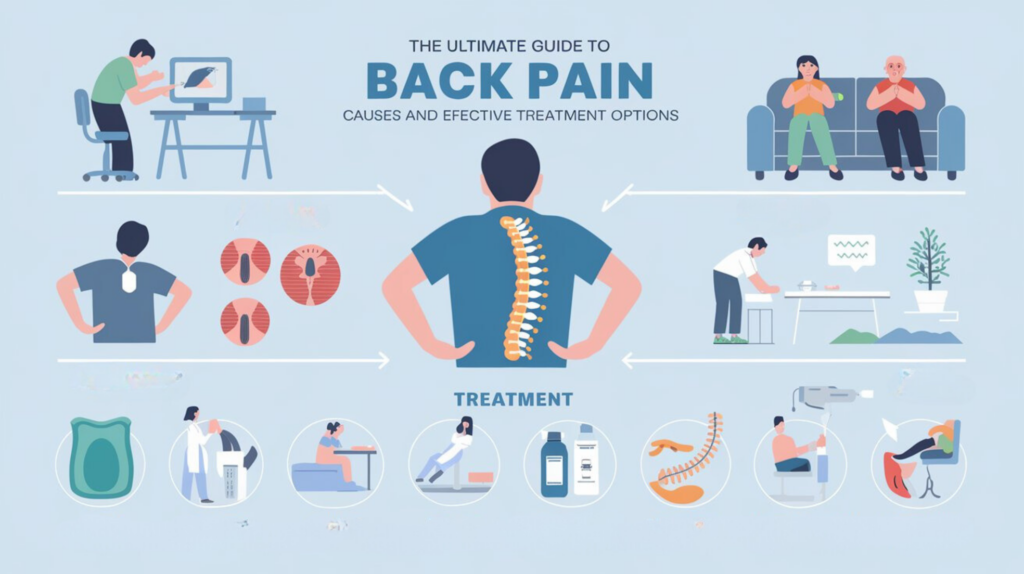
Back pain is one of the most common medical issues, affecting millions globally. Whether it’s a dull ache or sharp discomfort, back pain can significantly impact daily activities, work productivity, and overall quality of life. Understanding its causes and exploring effective treatments is key to managing this condition and preventing chronic pain. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common causes of back pain and how to treat them effectively.
1. Causes of Back Pain
a. Poor Posture
Poor posture is a leading cause of back pain, especially in today’s digital age, where many spend hours hunched over computers or mobile devices. Slouching strains the muscles and ligaments in your back, leading to discomfort over time.
How to Identify Poor Posture:
- Rounded shoulders or a hunched upper back.
- Head leaning forward beyond the natural alignment.
- Difficulty maintaining an upright position.
Preventive Measures:
- Practice ergonomic sitting and standing positions.
- Use a supportive chair that encourages proper posture.
- Take frequent breaks to stretch and correct your posture.
b. Muscle Strain or Sprain
Overexertion, improper lifting of heavy objects, or sudden awkward movements can cause muscle strain or ligament sprain. This type of back pain often resolves with rest but can worsen if ignored.
Symptoms:
- Localized pain or stiffness in the back.
- Pain that worsens with movement.
Treatment Tips:
- Apply ice or heat packs to reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help.
- Gentle stretching and physiotherapy promote healing.
c. Herniated Discs
A herniated or slipped disc occurs when the cushioning discs between vertebrae are displaced or damaged, often compressing nearby nerves.
Common Causes:
- Age-related wear and tear.
- Improper lifting techniques.
Symptoms:
- Pain radiating down the legs (sciatica).
- Numbness or tingling in the limbs.
Treatment Options:
- Physical therapy to strengthen the spine.
- Epidural steroid injections for pain relief.
- Surgical intervention in severe cases.
d. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity can weaken the muscles that support the spine, leading to chronic back pain.
Risk Factors:
- Prolonged sitting.
- Minimal exercise.
Solutions:
- Incorporate regular exercise like walking, swimming, or yoga.
- Use a standing desk or take frequent breaks if you work in a seated position.
e. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also lead to chronic back pain, including:
- Arthritis: Inflammation in the joints can affect the spine, causing stiffness and pain.
- Osteoporosis: Weak, brittle bones are more prone to fractures.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal curvature of the spine creates uneven pressure on the back muscles.
2. How to Treat Back Pain
a. Home Remedies
For mild to moderate back pain, home remedies can often provide significant relief:
- Rest and Recovery: Avoid strenuous activities for a few days, but don’t remain completely inactive, as prolonged rest can worsen stiffness.
- Heat and Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs in the first 48 hours to reduce swelling, then switch to heat packs to relax muscles.
- Gentle Stretches: Exercises like the cat-cow stretch or child’s pose can alleviate tension.
b. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is an effective, non-invasive treatment for various types of back pain. A trained therapist can design a personalized exercise program to:
- Strengthen the core and back muscles.
- Improve flexibility and posture.
- Reduce the risk of future injuries.
c. Medications
Pain and inflammation can be managed with both prescription and over-the-counter medications.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Reduce pain and ease inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: Alleviate muscle spasms.
- Topical Analgesics: Provide localized relief when applied to the affected area.
d. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments involve manual manipulation of the spine to improve alignment and reduce pain. This treatment is particularly effective for conditions like sciatica or misalignment-related discomfort.
e. Advanced Medical Interventions
For chronic or severe cases, advanced treatments may be necessary:
- Epidural Injections: Deliver steroids directly to the inflamed area.
- Surgery: Procedures like discectomy or spinal fusion are considered when other treatments fail.
f. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthier habits can prevent back pain and improve overall spine health:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight adds pressure to the spine.
- Stay Active: Engage in regular physical activity tailored to your fitness level.
- Focus on Nutrition: Calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone health.
3. When to See a Doctor
While most back pain resolves on its own, certain symptoms require medical attention:
- Persistent pain lasting more than a few weeks.
- Pain accompanied by fever, unexplained weight loss, or numbness.
- Difficulty controlling bladder or bowel movements.
4. Preventing Back Pain
Prevention is better than cure. Small changes can go a long way in protecting your back:
- Invest in Ergonomic Furniture: Ensure your workstation promotes good posture.
- Lift Properly: Bend at the knees and keep the object close to your body.
- Sleep Well: Use a supportive mattress and maintain a comfortable sleeping position.
Conclusion
Back pain can be debilitating, but it’s often manageable with the right approach. By understanding the causes and exploring a combination of treatments, you can regain control of your life and prevent recurring discomfort. Whether through simple lifestyle adjustments, professional therapy, or advanced medical interventions, relief from back pain is within reach. Prioritize your spine health today to enjoy a pain-free tomorrow!

